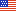
3.2.3 Estimate Signal SD
Some of the routines in DIFF_CALC require a measure of the noise in your images. This is either measured in the background of the b0 image, or automatically from the goodness of fit of your data. There are 4 options, which can be selected using the opt button to the right of the estimate signal SD button. The four options are as shown below:
The default option is an automatic estimation of the noise. The software masks an area of the brain that is known to be essentially free of physiological noise, in the white matter regions toward the top of the brain, based on the outlier probability maps found in Walker, et al1. Tensor fitting is performed on only these voxels in order to assess the goodness of the fit. A second option uses the GMM robust fitting to get a better estimate in the presence of artifactual data points. The user can input the fraction of outliers they wish to allow. Default value is 0.05 (i.e. 5%). A noise estimate is derived from each of these methods based on the formulation from Chang, et al2.
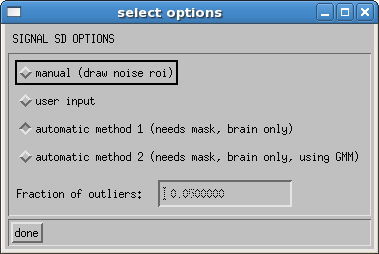
The user can also choose to manually draw an noise ROI. When you click the estimate signal SD button, a window will pop up that is similar to the display raw images window. Select a slice toward the top or bottom of the brain, where there is a significant amount of noise, which is generally free of artifacts. Click on the DRAW NOISE ROI button, then in the image, use the left mouse button to draw, and the right mouse button to close the ROI. An example is shown here:
As shown in this example, it is useful to adjust the gamma and max ceiling so that the background of the image is more visible. Additionally, the ROI is best placed in a region free of ghosting or other artifacts. If your images are reconstructed with parallel imaging techniques, make sure that you define your noise ROI in a region containing noise, not all zero values.
The final option is user input. In this case, the user is required to fill in a value for the noise. This can be measured any way the user deems appropriate. Note that if a value for noise exists in the .list file for your data, that value will be entered automatically, as shown in the example below. Simply replace the default value with the noise value you desire.
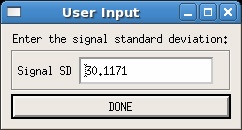
Once a noise value has been entered the mask raw images button should become available in the main GUI.
References
- Walker, L., Chang, L.-C., Koay, C. G., Sharma, N., Cohen, L., Verma, R., Pierpaoli, C. (2011). Effects of physiological noise in population analysis of diffusion tensor MRI data. Neuroimage 54(2):1168-1177.
- Chang, L.C., Walker, L., Pierpaoli, C., (2012) Informed RESTORE: A Method for Robust Estimation of Diffusion Tensor from Low Redundancy Datasets in the Presence of Physiological Noise Artifacts. Magn Reson Med. 68(5):1654–1663.